Overview
AUCMEDI integrates Automated Machine Learning (AutoML).
The mentality behind AutoML is to ensure easy application, integration and maintenance of complex medical image classification pipelines.
Especially for clinical scientists without a computer science background, research and application of state-of-the-art medical image classification approaches are a complex task. The majority of implementations are so called "island solutions", which are implemented and specialized for a single dataset without the possibility of fast reproducibility or even translational application on new datasets (even if it is the same image modality).
This situation lead to a frustration of clinicians that high performing models are existing but can not be applied without various pipeline modifications.
Thus, AUCMEDI wants to provide a fast and intuitive interface through AUCMEDI AutoML for building, application and sharing of state-of-the-art medical image classification models.
Wikipedia defines AutoML
AutoML potentially includes every stage from beginning with a raw dataset to building a machine learning model ready for deployment.
AutoML was proposed as an artificial intelligence-based solution to the growing challenge of applying machine learning.
The high degree of automation in AutoML aims to allow non-experts to make use of machine learning models and techniques without requiring them to become experts in machine learning. Automating the process of applying machine learning end-to-end additionally offers the advantages of producing simpler solutions, faster creation of those solutions, and models that often outperform hand-designed models.
AutoML Types in AUCMEDI¤
AUCMEDI offers two interfaces for automatic building and fast application of state-of-the-art medical image classification pipelines.
AutoML Overview of AUCMEDI
| AutoML Type | Required Software | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Command Line Interface (CLI) | Python & Dependencies | AUCMEDI application via command line script interaction in a local environment. Recommended for research settings. |
| Docker Image | Docker | AUCMEDI application via command line script interaction in a secure and isolated environment. Recommended for clinical settings. |
AutoML Application¤
The CLI as well as Docker interface both utilize the same AutoML modes and pipeline principles.
This means that providing the same parameters to either AutoML interface will result into an identical pipeline setup.
In a code-wise view, these two commands will perform the same operation:
# Run AUCMEDI AutoML via CLI (dataset in working directory)
aucmedi training --architecture "DenseNet121"
# Run AUCMEDI AutoML via Docker (dataset mounted via volume)
docker run \
-v /home/dominik/aucmedi.data:/data \
--rm \
ghcr.io/frankkramer-lab/aucmedi:latest \
training \
--architecture "DenseNet121"
It is also possible to train a model with CLI and compute predictions in a secure Docker environment. Especially in clinical settings, such setup is commonly applied.
An AutoML AUCMEDI call can always be splitted into 3 parts:
1) AutoML Type (program)
2) AutoML Mode
3) Parameters
Example
# AUCMEDI AutoML call
aucmedi training --architecture "MobileNetV2"
# Split into parts
aucmedi `# AutoML Type -> here CLI` \
training `# AutoML Mode -> here training` \
--architecture "MobileNetV2" `# Parameters -> here specific architecture`
AutoML Workflow¤
AUCMEDI offers three AutoML modes: training, prediction and evaluation.
Training:
The training mode fits a single or multiple models with fixed or self-adjusting hyper parameters.
Important hyper parameters as the neural network architecture or the general pipeline setup can be passed as arguments to the AutoML call.
The training process takes as input images with annotated classification (ground truth) and outputs the fitted model(s).
Prediction:
The prediction mode utilizes the fitted model(s) to infer the classification of unknown images. Hyper parameters, model weights and
general pipeline structure will be loaded from the model directory.
The prediction process takes as input unknown images and outputs a CSV file with prediction probabilities.
Evaluation:
The evaluation mode compares ground truth annotations with predicted classifications to estimate model performance.
The evaluation process takes as input images with annotated classification (ground truth) as well as predicted classifications,
and outputs various performance evaluation figures and metrics.
More information on parameters can be found here: AutoML - Parameters
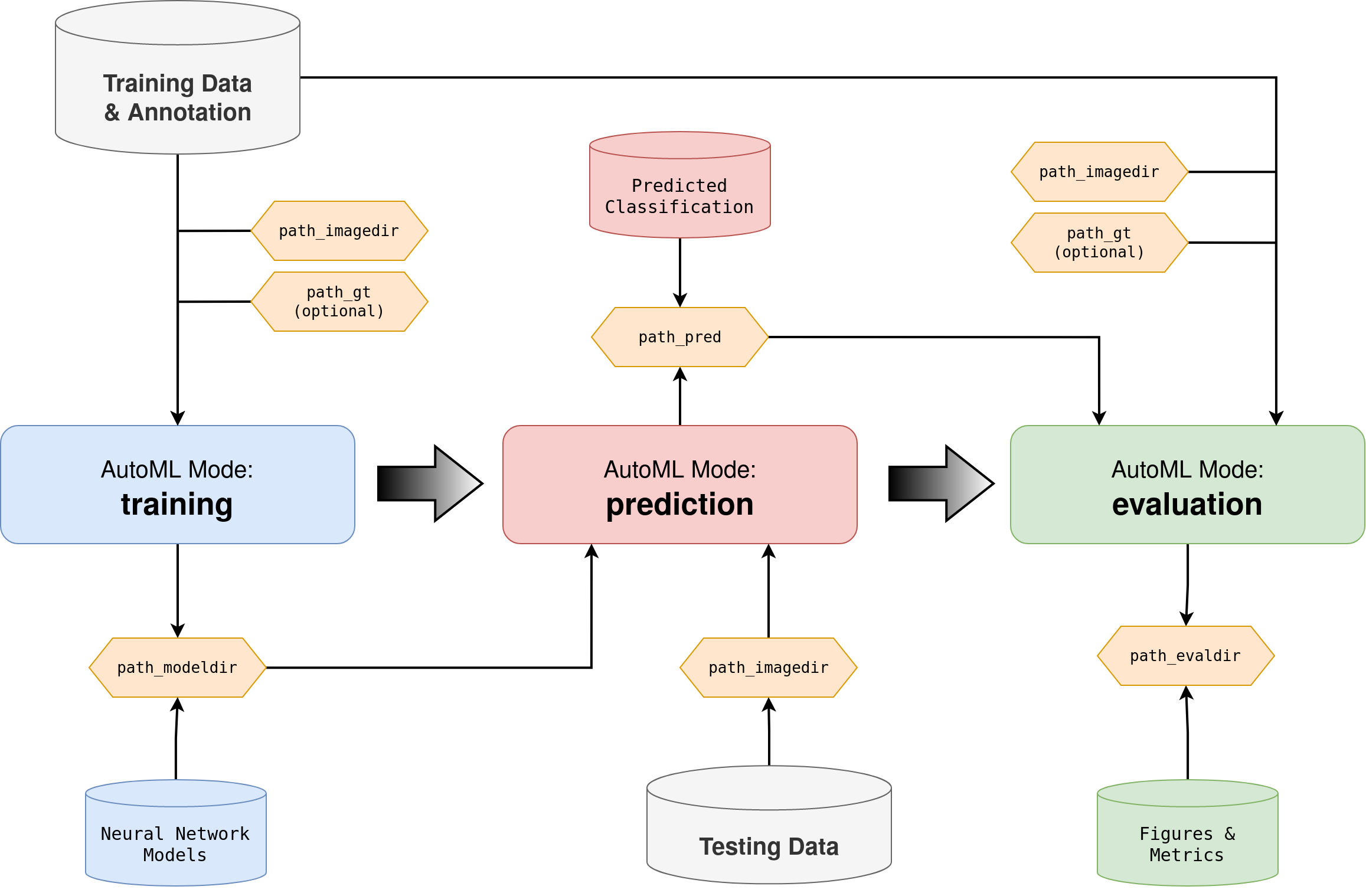 Flowchart diagram of AUCMEDI AutoML showing the pipeline workflow and three AutoML modes: training for model fitting, prediction for inference of unknown images, and evaluation for performance estimation.
Flowchart diagram of AUCMEDI AutoML showing the pipeline workflow and three AutoML modes: training for model fitting, prediction for inference of unknown images, and evaluation for performance estimation.